Difference between revisions of "Robotics: Principles and Practice - Software Installation Guide"
(→Option B: Install Required Tools and Utilities on a Computer running Ubuntu 20.04) |
(→Accessing Physical Devices) |
||
| Line 262: | Line 262: | ||
sudo apt-get update | sudo apt-get update | ||
catkin_make | catkin_make | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
= Accessing Physical Devices = | = Accessing Physical Devices = | ||
Revision as of 07:50, 16 July 2024
Contents
This page provides a step-by-step guide to installing the tools, utilities, and example software for Robotics: Principles and Practice on Ubuntu 20.04 with ROS Noetic.
Please follow these instructions exactly as they are stated. Do not be tempted to skip through them, assuming that you will be able to figure it out yourself. You might, but it is more likely you will miss something small but important and it won't work as required. Take your time, follow these instructions carefully, and everything will work.
There are two options:
- Option A: install the VirtualBox Ubuntu 16.04 virtual machine (VM) with everything pre-installed.
- Option B: install all the required tools and utilities directly on a computer running Ubuntu 20.04.
We cover both in the following, starting with Option A.
Option A: Install the VirtualBox Ubuntu 20.04 Virtual Machine
Install VirtualBox
There follows instructions for Windows, Mac OS, and Ubuntu (in case you already have Ubuntu but want to use the VM instead of installing all the required tools and utilities).
Windows
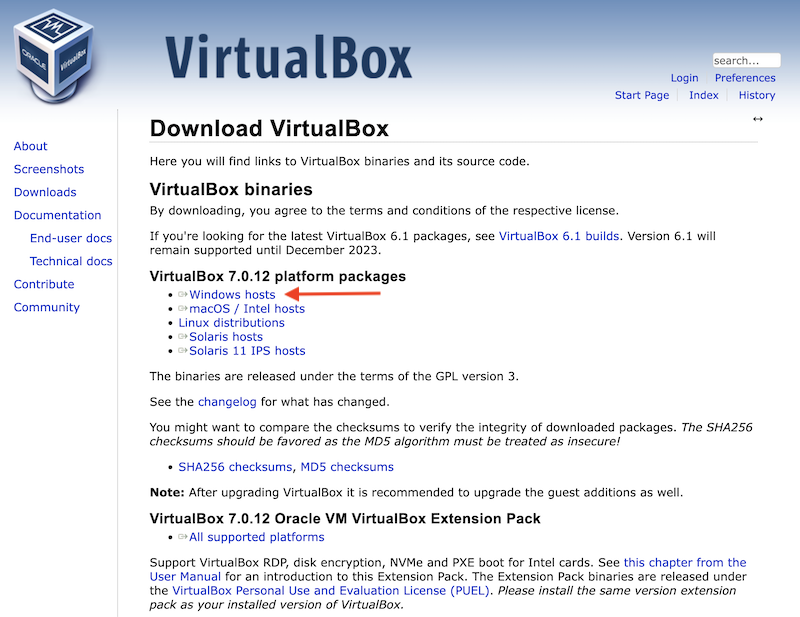
Open the VirtualBox Download page at https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads and select Windows hosts to download the installation file.
Double click on the downloaded file (VirtualBox-7.0.18-162988-Win.exe at time of writing) and follow the instructions.
MacOS
Download the .dmg installer for OS X systems, execute the file and follow the instructions.
If the VirtualBox installer fails as it is completing the installation, it is probably a problem with a security setting. Go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy. Click the lock to make changes (if necessary). Click the Allow button at the bottom and re-run the installer.
Ubuntu Linux
You can install VirtualBox via the Ubuntu Software Center or through command line as follows.
sudo apt update sudo apt install virtualbox
Install the VirtualBox Extension Pack
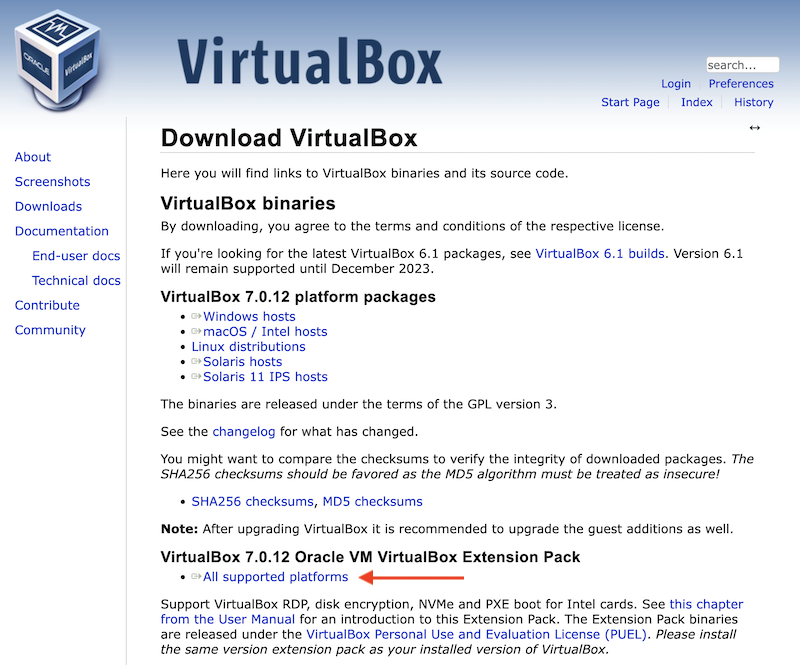
Select All supported platforms on the VirtualBox Download page to download the VirtualBox Extension Pack. This is needed to provide access to USB devices such as the Lynxmotion AL5D robot manipulator, iRobot Create 2 mobile robot, and webcams.
Double click on the downloaded file (Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-7.0.18.vbox-extpack at time of writing) and follow the instructions.
VirtualBox Setup
Step 1: Copy the Virtual Disk Image
The virtual disk image rpp-vm.20.04.vdi contains a VirtualBox virtual machine with Ubuntu 20.04, ROS Noetic, and example code pre-installed. It will be distributed on a physical disk. Copy it to some convenient, easily-identified folder.
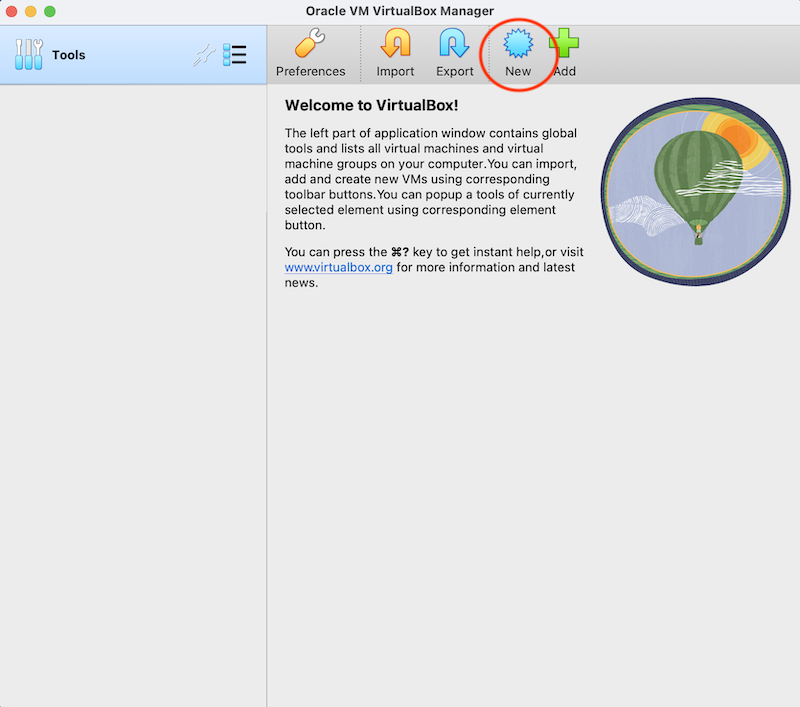
Step 2: Launch VirtualBox
In VirtualBox, you first need to create a new virtual machine. Click on the New button.
Usually the guided menu will open. Change to expert mode.
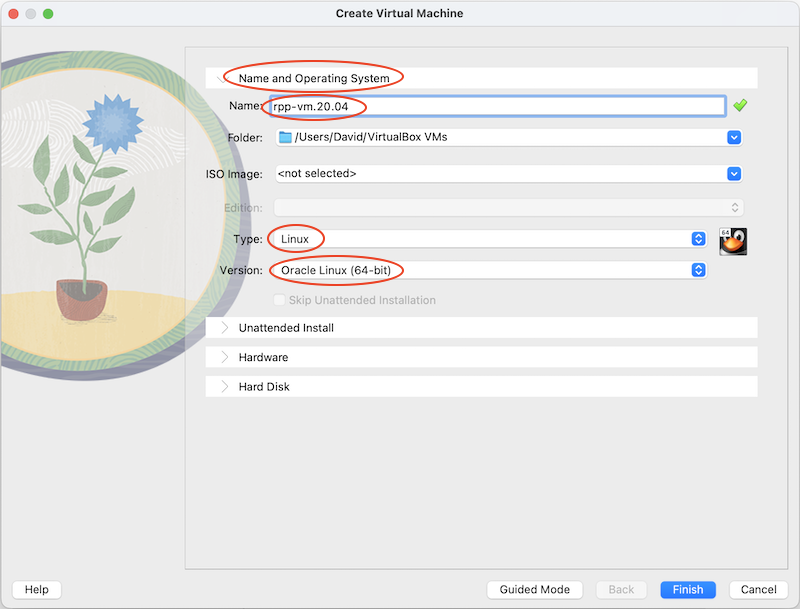
Step 3: Configure and create the virtual machine
If it's not already open, click the Name and Operating System tab
- Set the name to rpp-vm.20.04
- Select Linux for the operating system type
- Select Ubuntu (64-bit) for the operating system version
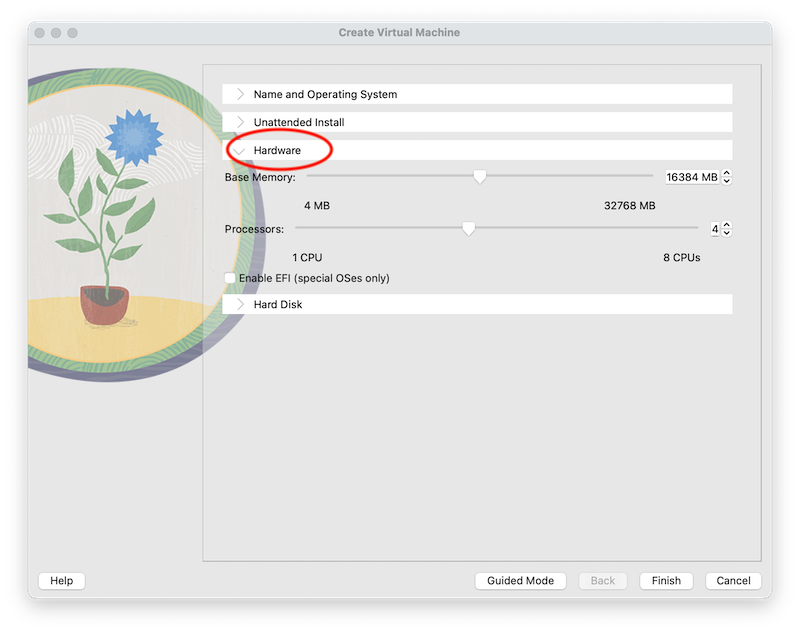
Click the Hardware tab.
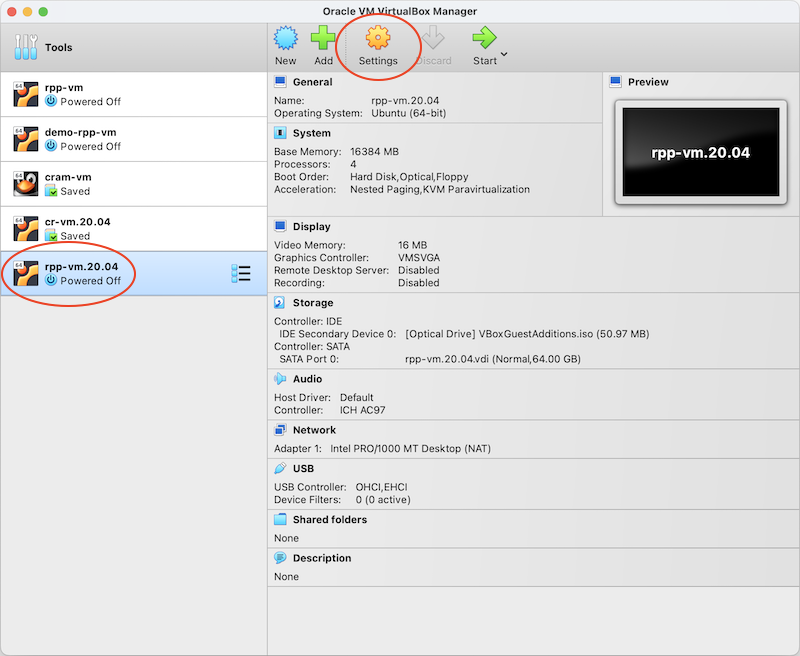
- Set the VM's memory size (RAM); choose 4096 MB or more if your PC's capacity allows. We set it to 16384 MB in the screenshot
- Set the number of processors to use. We set it to 4 in the screenshot.
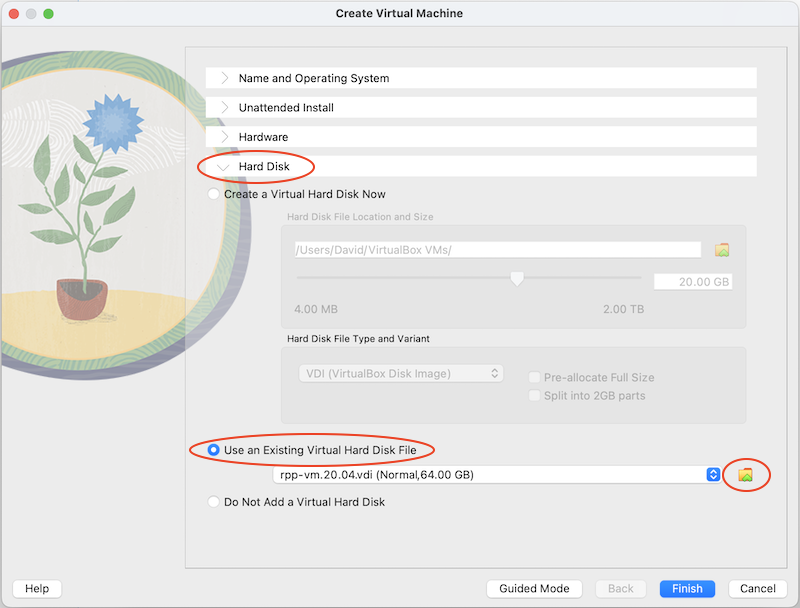
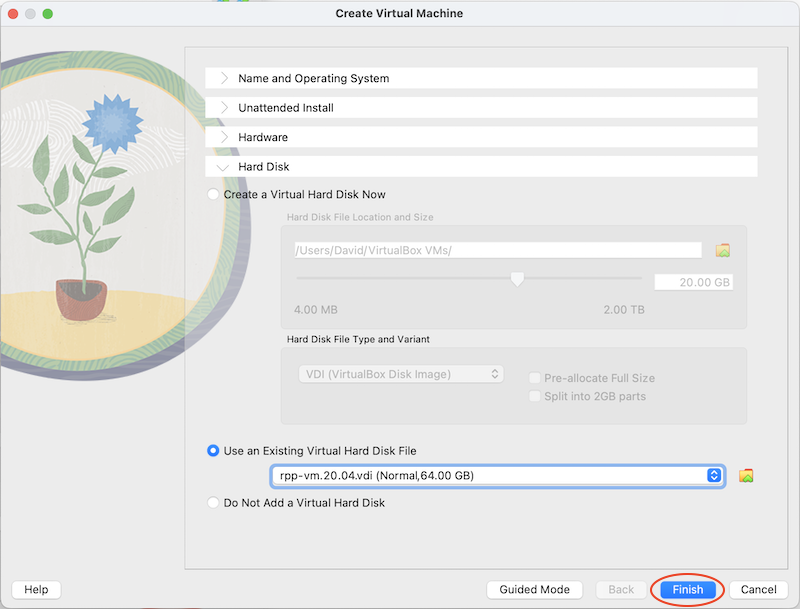
Click the Hard Disk Tab
- Select Use an Existing Virtual Hard Disk File
- Using the button on the right, open the file explorer
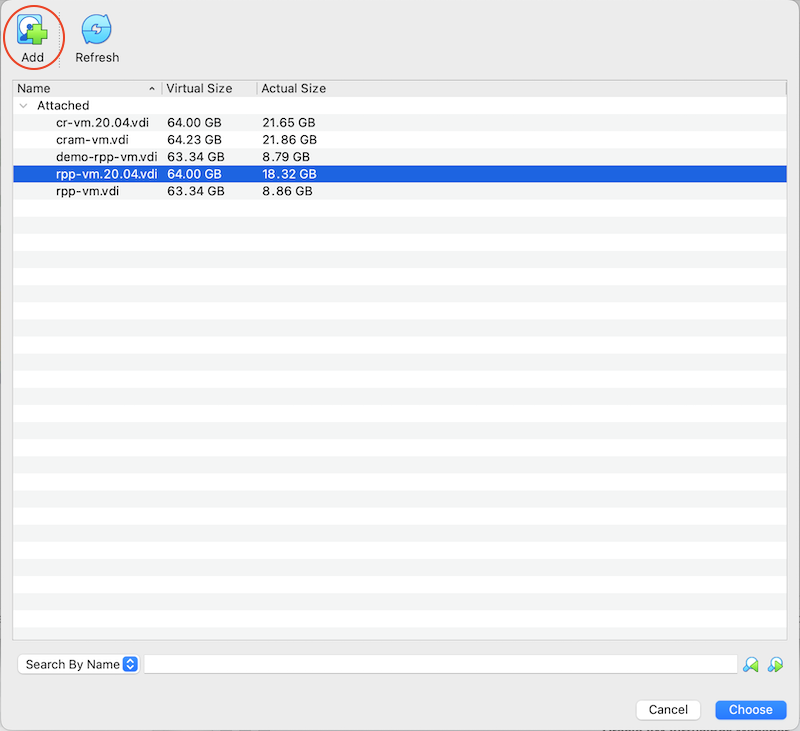
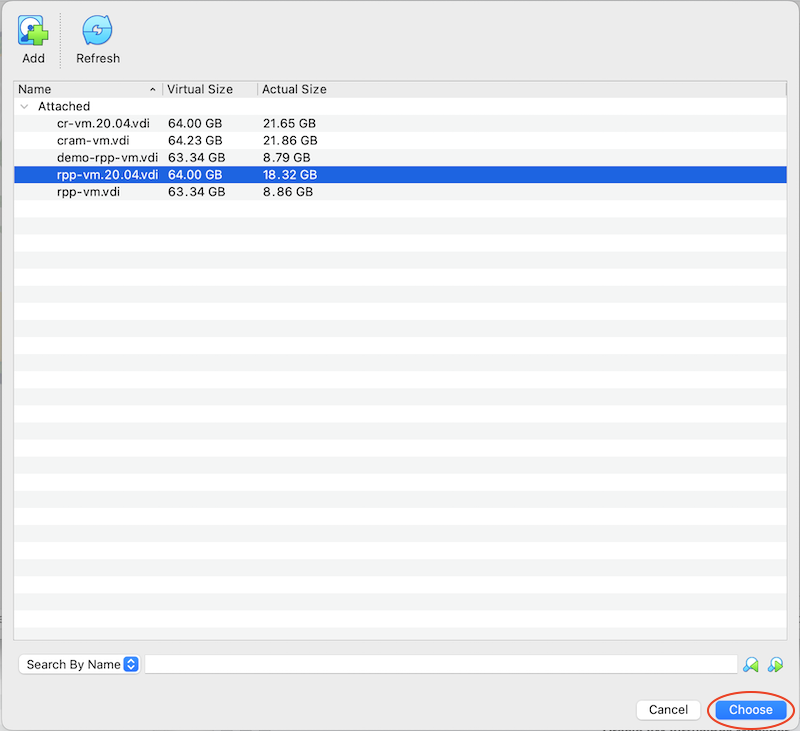
In the window that pops up, click Add
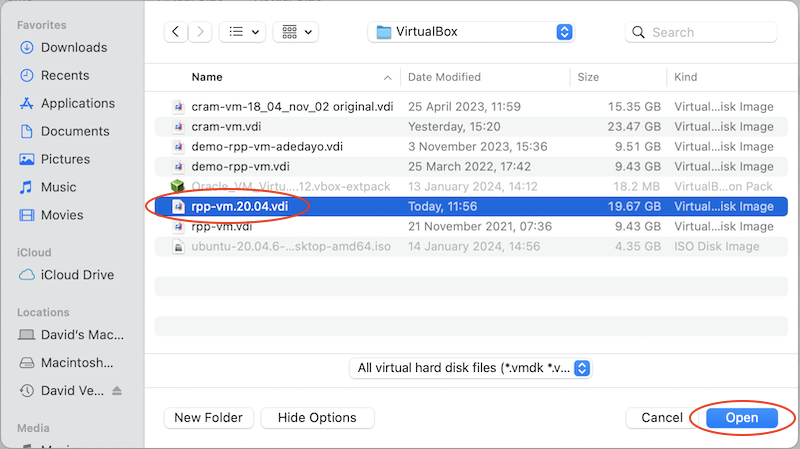
Browse to where you stored the rpp-vm.20.04.vdi file, select it, and click Open
Click Choose
Finally, click Finish
Step 4: Enable USB devices
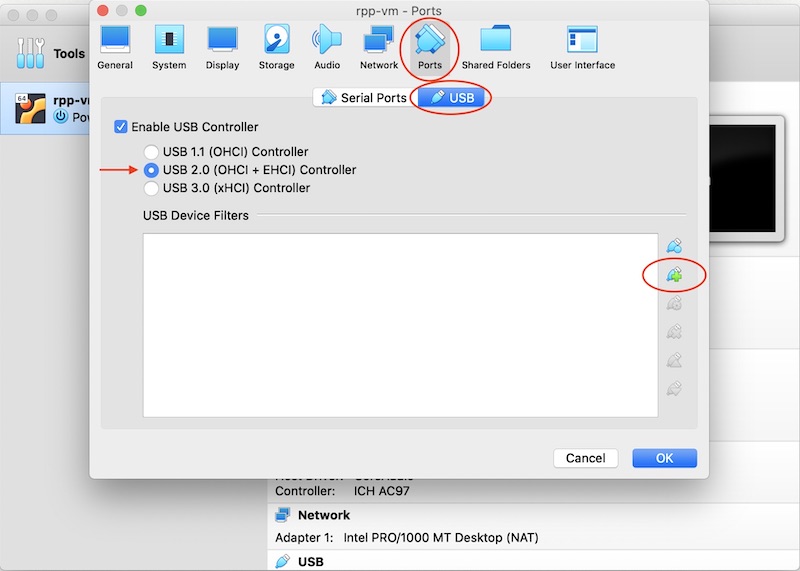
Choose the newly created virtual machine and click on Settings.
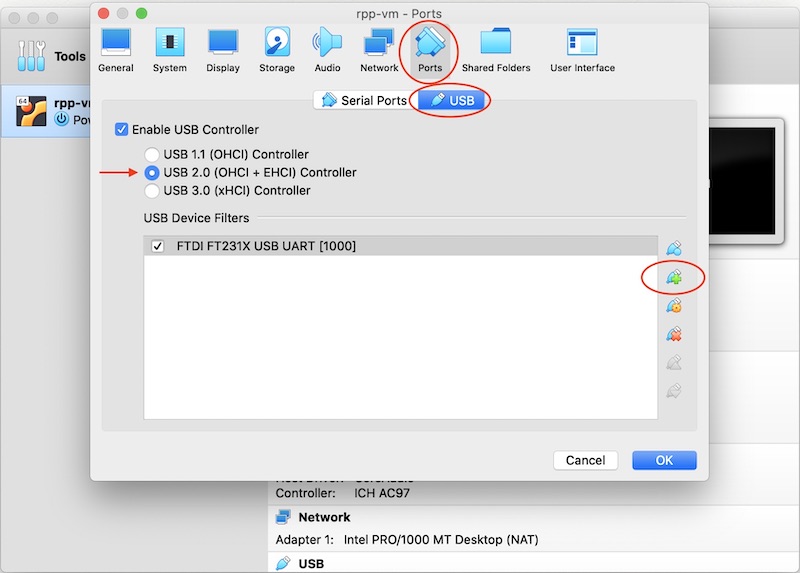
- Click on Ports.
- Click on USB and select USB 2.0.
- Choose the device you want to add from the list by clicking the connector icon with the green cross at the right hand side.
Notice that none of the devices you want to add, e.g., Lynxmotion AL5D robot manipulator, are in the list.
This is because the device needs to be connected before it can be added.
Here is what you would see if the iRobot Create 2 mobile robot was connected.
For now, just add your webcam and remember to return to this step when you want to use any USB device later in the course, e.g., an external webcam, the Lynxmotion AL5D robot manipulator, or the iRobot Create 2 mobile robot.
The device for the Lynxmotion AL5D robot manipulator is FTDI FT232R USB UART [0600].
The device for the iRobot Create 2 mobile robot is FTDI FT231X USB UART [1000].
Note: if your host operating system is Ubuntu, you should also enter the following in a terminal of your host machine and then restart the cram-vm virtual machine:
$ sudo adduser $USER vboxsf
Step 5: Enable Host OS to Guest OS Copy and Paste
When doing exercises and assignments, you may wish to copy text from the host OS (Windows 10, probably) and paste it to the guest OS (Ubuntu 18.04). Note that pasting to the terminal is <shift> <ctrl> v not <ctrl> v.
To do this, we need to enable Shared Clipboard and Drag’n’Drop functionality between Guest and Host Machine.
To enable Host OS to Guest OS Copy and Paste, Guest Additions must be installed in the virtual machine. This has already been done in the cram-vm virtual machine.
Power off your Ubuntu guest OS.
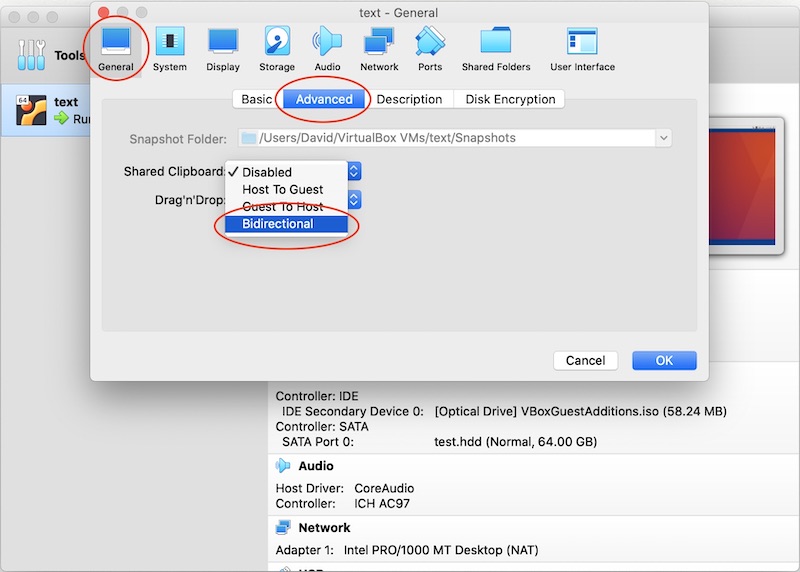
Choose the cram-vm virtual machine and click on Settings.
Click on General and Advanced and select Shared Clipboard and choose the Bidirectional option.
Select Shared Drag 'n' Drop and choose the Bidirectional option.
When you restart the virtual machine, double check that the copy and paste, and the drag and drop functionalities are enabled.
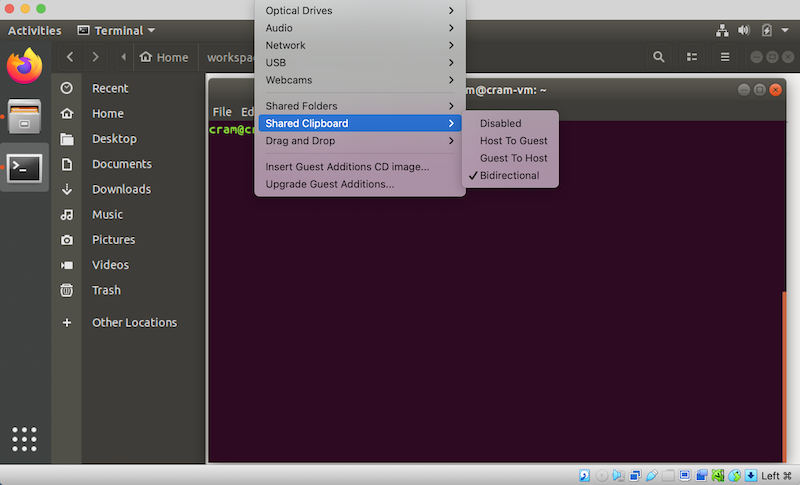
Click on Devices and Shared Clipboard and choose the Bidirectional option.
Now, click on Devices and Drag and Drop and choose the Bidirectional option.
Everything is set up and the virtual machine can now be started. When Ubuntu 20.04 boots, enter the password rpp, if asked.
Option B: Install Required Tools and Utilities on a Computer running Ubuntu 20.04
Install ROS Noetic
If a terminal is not already open, open one by typing ctrl-alt-t.
Copy and paste the installation commands below to the terminal and execute them by entering return.
Note: to copy from the browser use by ctrl-c or cmd-c. However, to paste them to the terminal use shift-ctrl-v (or right click and select paste).
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list' sudo apt install curl curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ros/rosdistro/master/ros.asc | sudo apt-key add - sudo apt update sudo apt install ros-noetic-desktop source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash echo "source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc sudo apt install python3-rosdep python3-rosinstall python3-rosinstall-generator python3-wstool build-essential sudo apt install python3-rosdep sudo rosdep init rosdep update
Install the Lynxmotion AL5D Gazebo Simulator ROS Package
Also see: https://github.com/cognitive-robotics-course
NB: There are errors with this installation - you can skip it if you wish
If a terminal is not already open, open one by typing ctrl-alt-t.
Copy and paste the installation commands below to the terminal and execute them by entering return.
sudo sh -c ' echo "deb http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo/ubuntu-stable `lsb_release -cs` main" >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/gazebo-stable.list' wget http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo.key –O –|sudo apt-key add - sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-joint-state-publisher ros-noetic-joint-state-publisher-gui \ ros-noetic-gazebo-ros-control ros-noetic-gazebo-ros ros-noetic-gazebo-dev ros-noetic-gazebo-msgs \ ros-noetic-gazebo-plugins ros-noetic-gazebo-ros-pkgs ros-noetic-effort-controllers \ ros-noetic-joint-state-controller ros-noetic-position-controllers ros-noetic-genpy sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-gazebo-ros # adding it to previous apt-get install didn't work mkdir -p ~/workspace/ros/src cd ~/workspace/ros/src git clone https://github.com/cognitive-robotics-course/lynxmotion_al5d_description.git cd .. catkin_make source devel/setup.bash echo "source $HOME/workspace/ros/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
Install the iRobot Create 2 ROS Package
We use the create_robot ROS package from Autonomy Lab, Simon Fraser University, to interface with the iRobot Create 2 mobile robot: https://github.com/AutonomyLab/create_robot.
Also refer to https://github.com/AutonomyLab/create_robot/blob/noetic/README.md
If a terminal is not already open, open one by typing ctrl-alt-t.
Copy and paste the installation commands below to the terminal and execute them by entering return.
sudo apt-get install python3-rosdep python3-catkin-tools mkdir -p ~/workspace/ros/src # if not done previously cd ~/workspace/ros/src git clone https://github.com/autonomylab/create_robot.git --branch noetic cd .. rosdep update
Install the Example Programs ROS Meta Package
This meta package comprises ROS packages for Modules 2, 3, 4, and 5 (module2, module3, module4, and module5, respectively).
If a terminal is not already open, open one by typing ctrl-alt-t.
Copy and paste the installation commands below to the terminal and execute them by entering return.
sudo apt-get install libncurses-dev # for module 5 roscd cd ../src git clone https://github.com/cognitive-robotics-course/coro_examples.git cd .. sudo apt-get update catkin_make
Accessing Physical Devices
For completeness, here are the instructions to access the iRobot Create 2 mobile robot and the Lynxmotion AL5D robot manipulator. Instructions for a USB camera will be added later. You can carry out these instructions when you have access to the robots and cameras in the lab.
If you are using the rpp-vm VM, don't forget to enable access to the USB ports; see Step 5 of VirtualBox Setup in Option A above.
Setup the Connection to the iRobot Create 2 Mobile Robot
1. Connect your computer to Create's 7-pin serial port.
2. Switch on the Create 2 by pressing the “Clean” button; it should light up green if the Create 2 is charged. If it lights up flashing amber, it needs to be charged first.
3. Open a terminal and launch the launch file
roslaunch create_bringup create_2.launch
The green light in the "Clean" button will turn off.
4. Check that everything is working, as follows.
Open a new terminal.
List the topics.
rostopic list
Check that the bumpers are working.
rostopic echo /bumper
Check that the motor control is working.
rostopic pub -1 /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist -- '[0.1, 0.0, 0.0]' '[0.0, 0.0, 0.5]'
rostopic pub /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist -r 1 -- '[0.1, 0.0, 0.0]' '[0.0, 0.0, -0.5]'
rostopic pub -r 10 /cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist '{linear: {x: 0.1, y: 0.0, z: 0.0}, angular: {x: 0.0,y: 0.0,z: 0.0}}'
5. Trouble shooting: if the robot does not move, do the following (recall that the superuser password is rpp).
sudo usermod -a -G dialout rpp
- Power down the virtual machine (or PC if you are running Ubuntu natively) and power it back up again for the permissions to take effect.
- Check that the device is connected by inspecting the message produced by the following command or by clicking on the small blue USB connector icon at the bottom of the Ubuntu window.
dmesg | grep -i FTDI
- If are using the
rpp-vmvirtual machine and your host operating system is Ubuntu, you should also enter the following in a terminal of your host machine and then restart the virtual machine:
$ sudo adduser $USER vboxsf
- If the virtual machine displays blank black screen, try pressing CTRL + F on your keyboard. It should then display the content.
Setup the Connection to the Lynxmotion AL5D Robot Manipulator
1. Switch on the robot.
2. Connect your laptop to the robot controller using the USB cable.
3. If you are using the rpp-vm VM, and if you have not already done so, add the robot controller USB device to the list of registered USB devices.
- You can do this by following the instructions in Step 5: Enable USB Devices of VirtualBox Setup in Option A above.
- Alternatively, select Devices on the top VirtualBox menu bar, then select USB from the drop-down menu, and then select USB Settings from the second drop-down menu.
- Choose the device you want to add from the list by clicking the connector icon with the green cross at the right hand side. The device for the Lynxmotion controller is
FTDI FT232R USB UART [0600]. - Ensure the box on the left of this USB Device Filter is ticked.
- Choose the device you want to add from the list by clicking the connector icon with the green cross at the right hand side. The device for the Lynxmotion controller is
4. Check that everything is working, as follows.
- Open a new terminal and run the following command. Joint 0, i.e. the joint at the base of the robot, should rotate to the centre position.
echo "#0P1610S250" > "/dev/ttyUSB0" % setpoint 1610 for joint 0 at speed 250
5.Trouble shooting: if the robot does not move, do the following (recall that the superuser password is rpp).
sudo usermod -a -G dialout rpp
- Power down the virtual machine (or PC if you are running Ubuntu natively) and power it back up again for the permissions to take effect.
- Check that the device is connected by inspecting the message produced by the following command or by clicking on the small blue USB connector icon at the bottom of the Ubuntu window.
dmesg | grep -i FTDI
- If are using the
rpp-vmvirtual machine and your host operating system is Ubuntu, you should also enter the following in a terminal of your host machine and then restart the virtual machine:
$ sudo adduser $USER vboxsf
- Repeat Step 4.
- If the virtual machine displays blank black screen, try pressing CTRL + F on your keyboard. It should then display the content.